Introduction
Overview of U.S. health spending and the role of the federal government
The U.S. healthcare system is a complex network of public and private entities that work together to provide healthcare services to the American population. At the heart of this system is the federal government, which plays a significant role in regulating, funding, and overseeing various aspects of healthcare.
One of the key responsibilities of the federal government is to administer healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. These programs provide healthcare coverage to specific groups of individuals, including the elderly, disabled, low-income individuals, and children from low-income families.
Factual Data: Health Spending Breakdown
According to the most recent data available, the National Health Expenditure (NHE) in 2022 grew by 4%. Medicare accounted for 13% of the total health spending, while Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) accounted for 10%. Other domestic health spending accounted for 4%, hospital and medical care for veterans was 2%, and global health accounted for 0.1%.
Comparatively, Social Security accounted for 21% of federal outlays in the fiscal year 2023, while defense accounted for 13%. It is important to note that mandatory spending constitutes the majority (88% or $1.6 trillion) of federal spending on health programs and services.
The Role of the Federal Government
The federal government’s involvement in healthcare goes beyond funding and administering specific programs. It also plays a crucial role in regulating healthcare practices, ensuring quality standards, and promoting health equity.
Regulations and guidance are put in place by the government to ensure that healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and nursing homes, meet certain standards of care. This includes regulations related to patient safety, infection control, and the protection of patient rights.
Additionally, the federal government is responsible for overseeing the coordination of benefits and recovery between different healthcare payers, such as Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurance companies. This helps to ensure that individuals receive the appropriate coverage and that healthcare costs are appropriately shared between payers.
Furthermore, the federal government is focused on improving healthcare outcomes and promoting innovation in care delivery. Initiatives such as the CMS Innovation Center and health equity programs aim to foster new approaches to healthcare, improve patient outcomes, and address health disparities.
Resources and Education
To support healthcare professionals and stakeholders, the federal government provides a range of training and education resources. The Medicare Learning Network (MLN) offers a wealth of educational materials and resources to help healthcare providers understand and navigate the Medicare program.
In addition, CMS (Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) has outreach resources aimed at improving health outcomes through partnerships with healthcare providers, community organizations, and patient advocacy groups. These resources provide valuable information on topics such as Medicare benefits, enrollment, and patient rights.
Data & Research
The federal government also plays a role in collecting and analyzing data on healthcare spending, trends, and patient outcomes. This data helps policymakers make informed decisions and shape healthcare policies that are evidence-based and efficient.
The National Health Expenditure Fact Sheet provides a valuable resource for understanding the current state of health spending in the United States. It offers insights into historical trends and breakdowns of spending by different sectors of the healthcare system.
In conclusion, the federal government plays a pivotal role in the U.S. healthcare system, providing funding, oversight, and regulations to ensure the delivery of quality healthcare services. Understanding the role of the federal government in healthcare is essential for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals to navigate this complex system effectively.
The Largest Shares of Total Health Spending
Breakdown of the largest contributors to U.S. health spending
When it comes to healthcare spending in the United States, two sectors take the lead – the federal government and households. Let’s take a closer look at how these two entities play a significant role in financing healthcare.
1. Federal government’s share (33%)
The federal government is the largest contributor to total health spending in the country, accounting for 33% of the total. Medicare, the federal health insurance program primarily for seniors, is responsible for 13% of the total health spending. It provides coverage for hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs for millions of Americans. Medicaid and CHIP, the joint state-federal programs that assist low-income individuals and families, account for another 10% of total health spending. These programs ensure that vulnerable populations have access to necessary healthcare services.
Moreover, the federal government also allocates funds for other domestic health spending, which accounts for 4% of the total. These funds support various healthcare initiatives, including research, public health campaigns, and disease prevention programs. Additionally, the government provides healthcare services for veterans, with hospital and medical care for veterans accounting for 2% of total health spending. Finally, the federal government contributes to global health initiatives, albeit to a lesser extent, with a share of 0.1%.
2. Households’ share (28%)
Households, including individuals and families, contribute significantly to total health spending in the United States. They account for 28% of the total spent on healthcare. This includes out-of-pocket expenses such as insurance premiums, deductibles, copayments, and any other costs that individuals bear directly. With rising healthcare costs, many households shoulder a considerable financial burden in meeting their healthcare needs. However, it is important to note that this 28% figure includes both insured and uninsured households.
Other contributors to U.S. health spending
While the federal government and households take the largest shares of total health spending, other entities also play a role. Private businesses contribute 18% of the total health spending, primarily through employer-sponsored health insurance plans. State and local governments account for 15% of the total health spending, financing programs such as Medicaid and public hospitals. Other private revenues, such as nonprofit organizations and foundations, contribute 7% to the overall health spending.
In conclusion, the federal government and households are the primary contributors to total health spending in the United States. With Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal health programs, the government ensures that essential healthcare services are provided to its citizens. Meanwhile, households bear a significant financial burden in meeting their healthcare needs. It is important to understand these breakdowns to gain insights into the funding sources of the U.S. healthcare system.
Mandatory Spending on Health Programs and Services
Analysis of federal spending on health programs and services
When it comes to federal spending on health programs and services in the United States, a significant portion is allocated to mandatory spending. This mandatory spending is not subject to annual appropriations votes by Congress, but instead mandated by existing laws. Let’s delve into the breakdown of federal spending on health programs and services and explore the importance of mandatory spending in the healthcare sector.
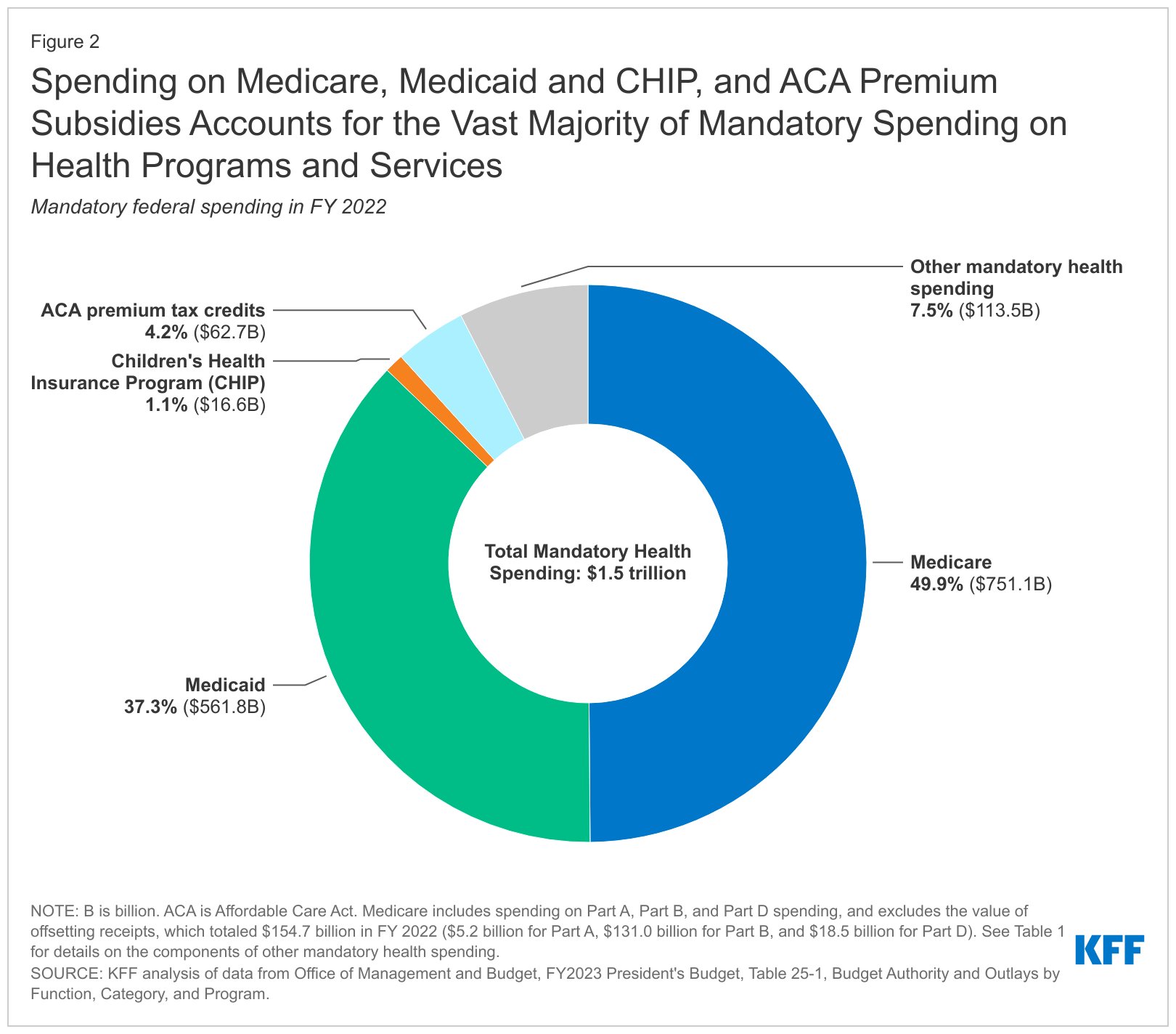
1. Majority of federal spending (88% or $1.6 trillion) categorized as mandatory spending
Out of the total federal spending on health programs and services, 88% or $1.6 trillion is classified as mandatory spending. This includes expenditures on Medicare, which is a federal health insurance program primarily for seniors, accounting for 53% ($979 billion) of the total mandatory spending. Medicare provides coverage for hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs for millions of Americans aged 65 and older.
Another significant portion of mandatory spending goes towards Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), which are joint state-federal programs. These programs assist low-income individuals and families in accessing healthcare services. Medicaid and CHIP account for 25% ($458 billion) of the total mandatory spending on health programs and services.
Additionally, mandatory spending includes the refundable portion of the health insurance premium tax credit for coverage through the ACA Marketplaces. This tax credit helps individuals and families afford health insurance plans purchased through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplaces. The refundable portion of this credit contributes to the overall mandatory spending.
2. Importance of mandatory spending in the healthcare sector
Mandatory spending plays a crucial role in ensuring access to healthcare programs and services for vulnerable populations. By mandating the allocation of funds to Medicare, Medicaid, CHIP, and the ACA Marketplaces, the government ensures that essential healthcare services are provided to those who need them the most.
Medicare, as the largest component of mandatory spending on health programs and services, ensures that seniors have access to vital healthcare services in their later years. This includes hospital care, physician visits, and prescription medications. Similarly, Medicaid and CHIP provide crucial support to low-income individuals and families, helping them afford necessary healthcare and ensuring their well-being.
The refundable portion of the health insurance premium tax credit for coverage through the ACA Marketplaces further expands access to quality healthcare. By providing financial assistance to eligible individuals and families, it helps to make health insurance more affordable and accessible.
Furthermore, mandatory spending on health programs and services also supports public health initiatives, medical research, disease prevention programs, and healthcare services for veterans. These investments contribute to the overall health and well-being of the population.
In conclusion, a significant portion of federal spending on health programs and services in the United States is categorized as mandatory spending. This funding is crucial in ensuring access to essential healthcare services for seniors, low-income individuals and families, and other vulnerable populations. By understanding the breakdown of federal spending, we can gain insights into the funding sources of the healthcare system and the importance of mandatory spending in supporting the well-being of the nation.
Growth of U.S. Health Care Spending
Comparison of the growth rate of U.S. health care spending in recent years
The growth of health care spending in the United States has been a topic of concern in recent years. The following sections provide an overview of the growth rates and comparisons of health care spending in the country.
1. Increase of 4.1% to reach $4.5 trillion in 2022
In 2022, health care spending in the United States reached $4.5 trillion, representing a 4.1% increase from the previous year. This substantial growth reflects the continuous rise in health care costs and increased utilization of health care services. On a per-person basis, health care spending amounted to $13,493 in 2022.
Examining the different contributors to health care spending, Medicare, the federal health insurance program primarily for seniors, saw a growth of 5.9% and reached $944.3 billion in 2022. Medicaid, the joint state-federal program for low-income individuals and families, experienced a significant growth of 9.6% and reached $805.7 billion. Additionally, private health insurance spending grew by 5.9% and reached $1,289.8 billion in 2022. Out-of-pocket spending, which includes expenses not covered by insurance, grew by 6.6% and totaled $471 billion.
2. Comparison with the growth rate of 3.2% in 2021
The growth rate of health care spending in 2022 is higher compared to the previous year. In 2021, health care spending increased by 3.2%, reaching a total of $4.35 trillion. This indicates a higher rate of growth in health care spending, reflecting the increasing demand for health care services and the rising costs associated with providing those services.
By comparing the growth rates between 2021 and 2022, it is evident that health care spending in the United States continues to rise at an accelerated pace. The higher growth rate in 2022 can be attributed to various factors, including increased utilization of health care services due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and the increasing cost of medical treatments and technologies.
In conclusion, the growth of health care spending in the United States has been substantial in recent years. The increase of 4.1% in 2022, reaching $4.5 trillion, highlights the continued rise in health care costs and utilization. Comparing the growth rates with the previous year, it is clear that health care spending is experiencing an upward trend. This emphasizes the need for policymakers, health care providers, and individuals to address the challenges associated with the rising costs of health care in order to ensure the sustainability and accessibility of quality health care services for all Americans.
Federal Subsidies for Health Insurance
Estimation and significance of federal subsidies for health insurance
Federal subsidies play a crucial role in providing financial assistance for health insurance coverage in the United States. These subsidies help individuals and families afford insurance plans and ensure access to necessary healthcare services. In 2023, it is estimated that federal subsidies for health insurance will reach $1.8 trillion, equivalent to 7.0% of the country’s GDP.
1. Expected federal subsidies in 2023: $1.8 trillion or 7.0% of GDP
The upcoming year is projected to see a significant increase in federal subsidies for health insurance. These subsidies encompass various forms of financial assistance, including premium tax credits, cost-sharing reductions, and subsidies for insurance coverage through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplaces.
Premium tax credits are designed to lower the cost of monthly insurance premiums for individuals and families with low to moderate incomes. Cost-sharing reductions, on the other hand, help individuals afford out-of-pocket expenses such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. These subsidies are vital in ensuring that healthcare coverage remains affordable for those who may not have access to employer-sponsored plans or government programs like Medicaid or Medicare.
Furthermore, federal subsidies for insurance coverage through the ACA Marketplaces have been instrumental in expanding access to healthcare for millions of Americans. These subsidies act as a safety net, allowing individuals and families to obtain affordable coverage even if they do not qualify for other healthcare programs. The estimated $1.8 trillion in federal subsidies in 2023 demonstrates the government’s commitment to making healthcare accessible and affordable for all.
2. Importance of subsidies in improving access to healthcare
Federal subsidies for health insurance play a critical role in improving access to healthcare for individuals and families across the United States. By reducing the financial burden associated with insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, these subsidies enable more people to obtain and maintain insurance coverage, resulting in better access to necessary healthcare services.
Without federal subsidies, many individuals and families would struggle to afford insurance coverage and may be forced to forgo necessary medical care. This can lead to delayed or inadequate treatment, resulting in negative health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run. Additionally, the availability of subsidies through the ACA Marketplaces has expanded coverage options for those who may have otherwise remained uninsured or underinsured.
By making health insurance more affordable and accessible, federal subsidies contribute to a healthier population and a more sustainable healthcare system. They help protect individuals and families from the financial burden of medical expenses and ensure that everyone has the opportunity to receive the care they need when they need it.
In conclusion, federal subsidies for health insurance are instrumental in improving access to healthcare and ensuring affordability for individuals and families in the United States. The estimated $1.8 trillion set to be allocated towards subsidies in 2023 demonstrates the significant investment made by the government to make healthcare coverage accessible to all Americans. These subsidies play a vital role in reducing financial barriers and ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to receive necessary healthcare services.
Federal Government Spending on Health
Insight into federal government spending on health
Federal government spending on health plays a significant role in the overall healthcare landscape in the United States. This section provides an overview of the expenditure and impact of federal spending on health.
1. Expenditure of nearly $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2019
In fiscal year 2019, the federal government allocated approximately $1.2 trillion for health-related programs and services. This represents a substantial amount of financial resources aimed at ensuring the well-being of the American population. The majority of federal spending on health programs falls into the category of mandatory spending, accounting for 88% or $1.6 trillion of the total.
Medicare, the federal health insurance program primarily for seniors, accounted for 13% of the total federal health spending in fiscal year 2019. Medicaid and CHIP, the joint state-federal programs for low-income individuals and families, accounted for 10% of the total. Other domestic health spending was responsible for 4% of the allocation, while hospital and medical care for veterans accounted for 2%. Global health initiatives received 0.1% of the federal health spending.
Comparing federal spending on health programs to other major areas of expenditure, Social Security accounted for 21% of federal outlays in fiscal year 2019, while defense accounted for 13%. This highlights the significant investment made by the federal government in ensuring the health and well-being of its citizens.
2. Impact of federal spending on the healthcare system
Federal spending on health has a substantial impact on the healthcare system in the United States. The allocation of financial resources towards mandatory spending on health insurance programs like Medicare and Medicaid ensures that eligible individuals have access to essential healthcare services.
Discretionary spending on federal agencies such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) plays a crucial role in promoting public health, advancing medical research, and ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications and medical devices.
Furthermore, federal spending on health programs and services not only supports the medical needs of vulnerable populations but also stimulates the economy by creating jobs within the healthcare sector.
In conclusion, federal government spending on health is a significant investment that contributes to the overall well-being of the American population. The expenditure of nearly $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2019 highlights the commitment of the federal government to ensure access to essential healthcare services. The impact of federal spending on the healthcare system extends beyond the provision of healthcare, encompassing public health initiatives, medical research, and economic stimulation. By understanding and addressing the challenges associated with rising healthcare costs, policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals can work towards ensuring the sustainability and accessibility of quality healthcare services for all Americans.
Income Tax Expenditures for Health Care
Explanation of income tax expenditures related to health care
Income tax expenditures are tax deductions, exclusions, and credits that reduce the amount of income tax owed by individuals or businesses. These expenditures are designed to incentivize certain activities or behaviors that are deemed beneficial to society. In the realm of health care, income tax expenditures play a crucial role in promoting affordability and access to medical services.
1. Total income tax expenditures: $234 billion
In the United States, income tax expenditures for health care amounted to $234 billion in the fiscal year 2019. These tax expenditures represent a significant investment by the government in ensuring access to health care services for individuals and families.
The largest component of income tax expenditures for health care is the tax exclusion for employer-sponsored health insurance. This exclusion allows individuals to exclude the value of employer-provided health insurance from their taxable income. In fiscal year 2019, this tax expenditure amounted to approximately $178 billion, making it the primary driver of income tax expenditures for health care.
Other notable income tax expenditures for health care include the deduction for medical expenses, the tax exclusion for contributions to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), and the credit for small employer health insurance premiums. These tax provisions aim to alleviate the financial burden associated with medical expenses and encourage individuals to save for future health care needs.
2. Role of tax incentives in promoting healthcare affordability
Tax incentives in the form of income tax expenditures play a vital role in promoting the affordability of health care services. By reducing the tax liability of individuals and businesses, these incentives make it easier for people to access and afford necessary medical treatments and services.
The tax exclusion for employer-sponsored health insurance, in particular, helps to make health insurance coverage more affordable for individuals and their families. By enabling employers to provide health insurance to their employees on a pre-tax basis, this provision reduces the out-of-pocket costs associated with obtaining health insurance coverage. It also ensures that individuals can access essential health care services without incurring significant financial strain.
Similarly, deductions for medical expenses and tax exclusions for contributions to HSAs allow individuals to offset the cost of medical care and save for future health care needs on a tax-advantaged basis. These provisions provide individuals with the flexibility to manage their health care expenses more effectively and promote personal responsibility for health care costs.
In conclusion, income tax expenditures for health care have a significant impact on the affordability and accessibility of medical services in the United States. With a total expenditure of $234 billion in fiscal year 2019, these tax incentives help individuals and families afford health insurance coverage and offset the cost of medical expenses. By understanding the role of tax incentives in promoting healthcare affordability, policymakers can continue to develop effective strategies that ensure the sustainability of the health care system and improve the overall well-being of the American population.
Overall Contribution of Federal Government
Discussion on the overall funding provided by the federal government
When examining the healthcare landscape in the United States, it is essential to consider the significant contribution of the federal government. The federal government plays a crucial role in funding various health programs and services, allocating a substantial amount of financial resources to ensure the well-being of the American population.
1. Assessment of the significant role played by federal funding
In fiscal year 2019, the federal government allocated approximately $1.2 trillion for health-related programs and services. This extensive expenditure demonstrates the commitment of the federal government to providing access to essential healthcare services for its citizens. The majority of federal spending on health programs falls into the category of mandatory spending, accounting for 88% or $1.6 trillion of the total.
Medicare, the federal health insurance program primarily for seniors, accounted for 13% of the total federal health spending in fiscal year 2019. This program ensures that eligible seniors have access to quality healthcare services. Medicaid and CHIP, the joint state-federal programs for low-income individuals and families, accounted for 10% of the total federal health spending. These programs provide vital support to vulnerable populations, helping them access necessary medical care.
Moreover, federal spending on health extends beyond insurance programs. Other areas of expenditure include domestic health spending, which accounted for 4% of the allocation, hospital and medical care for veterans (2%), and global health initiatives (0.1%). Each of these areas receives financial backing to address specific healthcare needs and promote well-being.
Comparatively, federal spending on health programs can be juxtaposed with other major areas of expenditure. Social Security, for instance, accounted for 21% of federal outlays in fiscal year 2019, highlighting the significant investment made by the federal government in ensuring the health and well-being of its citizens. Defense spending, on the other hand, accounted for 13% of federal outlays.
2. Importance of sustainable financing for a robust healthcare system
The impact of federal spending on health programs extends beyond providing healthcare services. It plays a vital role in promoting public health, advancing medical research, and ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications and medical devices. Discretionary spending on federal agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, the Food and Drug Administration, and the Health Resources and Services Administration, contributes to these efforts.
Sustainable financing is crucial for the long-term viability of the healthcare system. Rising healthcare costs and the increasing demand for healthcare services pose significant challenges. By understanding and addressing these challenges, policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals can work towards ensuring the sustainability and accessibility of quality healthcare services for all Americans.
In conclusion, the federal government’s significant contribution to healthcare through funding and programs is vital. The allocation of nearly $1.2 trillion in fiscal year 2019 demonstrates the commitment to ensure access to essential healthcare services. Whether through mandatory spending on health insurance programs or discretionary spending on federal agencies, federal funding plays a pivotal role in promoting the health and well-being of the American population. By addressing challenges and promoting sustainable financing, stakeholders can work together to create a robust and accessible healthcare system for all.
Conclusion and Future Considerations
Summary of the federal government’s role in U.S. health spending
The federal government plays a crucial role in funding healthcare programs and services in the United States. In fiscal year 2019, approximately $1.2 trillion was allocated for health-related programs, with the majority being mandatory spending. Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP accounted for significant portions of federal health spending, providing essential access to healthcare for seniors and low-income individuals and families. Other areas of expenditure included domestic health spending, hospital and medical care for veterans, and global health initiatives.
1. Recap of key findings on federal funding
– The federal government allocated around $1.2 trillion for health-related programs in fiscal year 2019.
– Mandatory spending accounted for the majority of federal health spending, totaling $1.6 trillion.
– Medicare accounted for 13% of the federal health spending, while Medicaid and CHIP accounted for 10%.
– Other areas of expenditure included domestic health spending (4%), hospital and medical care for veterans (2%), and global health initiatives (0.1%).
– Social Security accounted for 21% of federal outlays, while defense accounted for 13%.
2. Potential future developments and implications for healthcare in the U.S.
Sustainable financing is crucial for the long-term viability of the U.S. healthcare system. As healthcare costs continue to rise and demand for services increases, policymakers and stakeholders need to address these challenges. Additionally, advancements in medical research, public health initiatives, and regulation of medications and medical devices rely on discretionary spending on federal agencies.
Looking ahead, potential future developments include:
1. Healthcare reform efforts: Policymakers may explore ways to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare spending, ensuring equal access to quality healthcare for all Americans.
2. Innovation in healthcare delivery: The use of technology and new models of care can transform the healthcare landscape, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
3. Addressing healthcare disparities: Efforts to reduce disparities in healthcare access and outcomes among different populations will continue to be a priority.
4. Public health investments: Investing in public health initiatives can help prevent and manage diseases, promoting better population health.
Considering these potential developments, it is crucial to maintain a sustainable funding mechanism for healthcare programs and services. Collaboration between policymakers, healthcare providers, and individuals is necessary to create a robust and accessible healthcare system that meets the needs of all Americans.
In conclusion, the federal government’s significant contribution to healthcare financing and programs is vital for ensuring access to essential healthcare services. By recapitulating key findings on federal funding and considering potential future developments, stakeholders can work towards a healthcare system that promotes equitable access, advances medical innovations, and addresses healthcare disparities.



